Neoplastic Musculoskeletal Disease
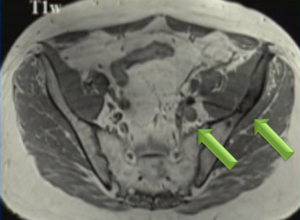
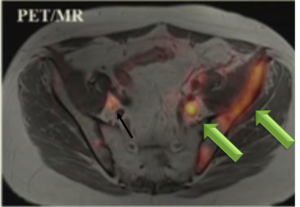
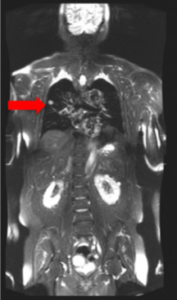
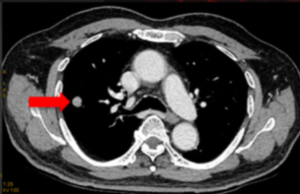
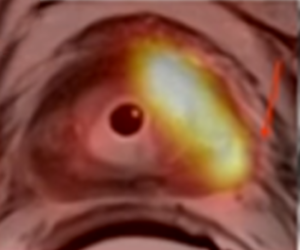
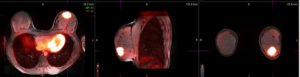
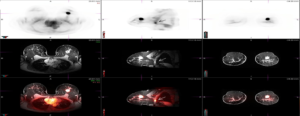
60-year-old man with history of multiple myeloma who underwent chemotherapy and had laboratory evidence of relapse.
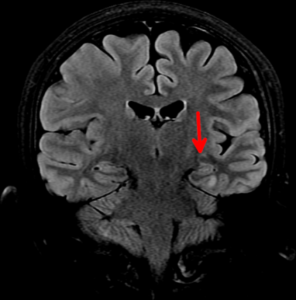
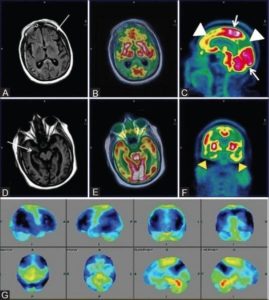
(A) whole-body low-dose CT shows subtle area of soft-tissue density in proximal left femoral shaft, (B) without corresponding osteolysis. (C) Subsequent FDG PET/MRI shows T1-hypointense marrow-replacing lesion in same location with increased FDG activity seen on fused PET/MR image (D), consistent with active disease.
CT often fails to detect early focal lesions that are not yet lytic. Owing to high soft tissue contrast and better ability to detect marrow lesions, whole body MRI has also been used for the evaluation of multiple myeloma
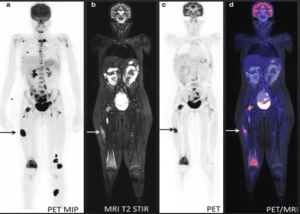
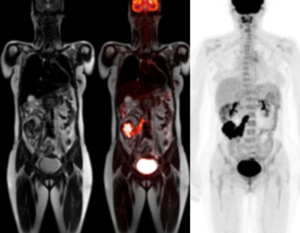
A 13-year-old girl with neurological symptoms and pain in the right knee.
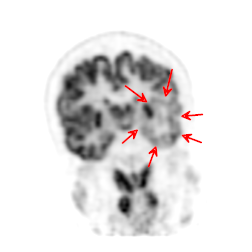
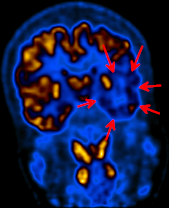
(A) PET MIP demonstrates widespread foci of FDG-accumulation suspected for disseminated malignancy. (B–D) Coronal MRI T2 fat sat, FDG-PET, and fused PET-MR show soft tissue and BM lesions.
- Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
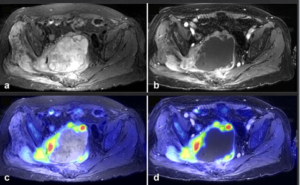
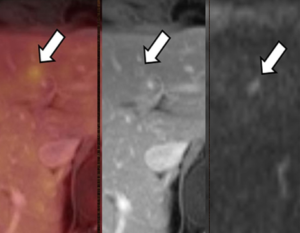
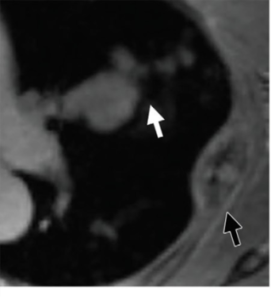
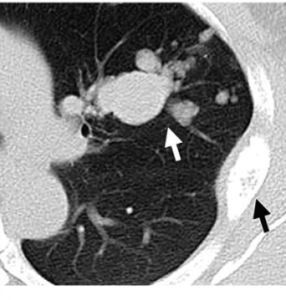
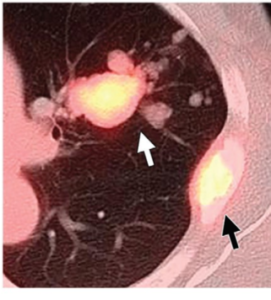
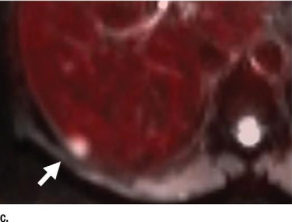
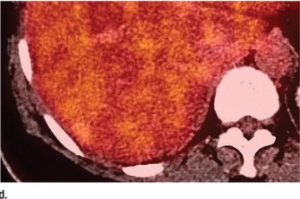
61-year-old female with a large pelvic mass discovered on CT and non-diagnostic biopsies taken during laparoscopic exploration.
(A) T2-weighted fat-saturated (FS) (B) FS post-gadolinium spoiled gradient recalled (SPGR) demonstrate a large heterogeneously T2-hyperintense pelvic mass extending through the right sciatic notch with peri-lesional edema and extensive central necrosis. Corresponding fused T2-weighted FS. (B) FS post-gadolinium SPGR FDG PET-MRI (D) images demonstrate intense peripheral FDG activity. An FDG-avid area was targeted during subsequent CT-guided biopsy, with pathology showing a high-grade malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
Non-Neoplastic Musculoskeletal Disease\
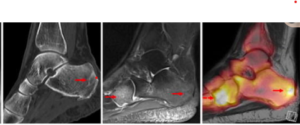
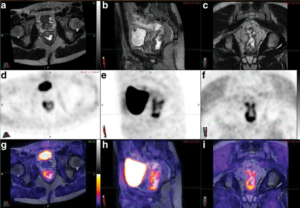
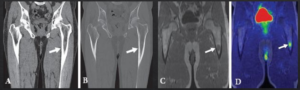
CT show sclerotic lesions in the dorsal calcaneus and degenerative changes in talonavicular region but no signs of acute stress fractures. On MRI, a fracture line in the dorsal calcaneus due to an older stress fracture that corresponds to elevated 18F-NaF PET uptake & Additionally, another stress fracture is shown on PET-MRI in the mediodorsal parts of the cuboid with elevated uptake on 18F NaF PET .
MRI provides high-resolution anatomical images to assess structural changes for diagnosis and staging of RA disease. Hybrid PET-MRI systems offer to combine high-resolution morphologic images with early molecular markers to enhance the study of RA.
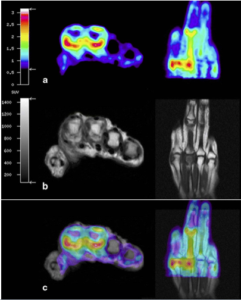
Hand in early RA acquired on an integrated PET-MRI system, The highest uptake is seen at the palmer portion of the second metacarpophalangeal joint which corresponds to synovial thickening and contrast enhancement on MRI.